Food Waste
Extent of the Problem
Global Scale: Food waste occurs throughout the entire food supply chain, from production and processing to distribution, retail, and consumption.
Quantities: According to estimates, about one-third of the food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally each year.
Carbon Footprint
Raw Material Footprint: 29% of England's raw material footprint was food.
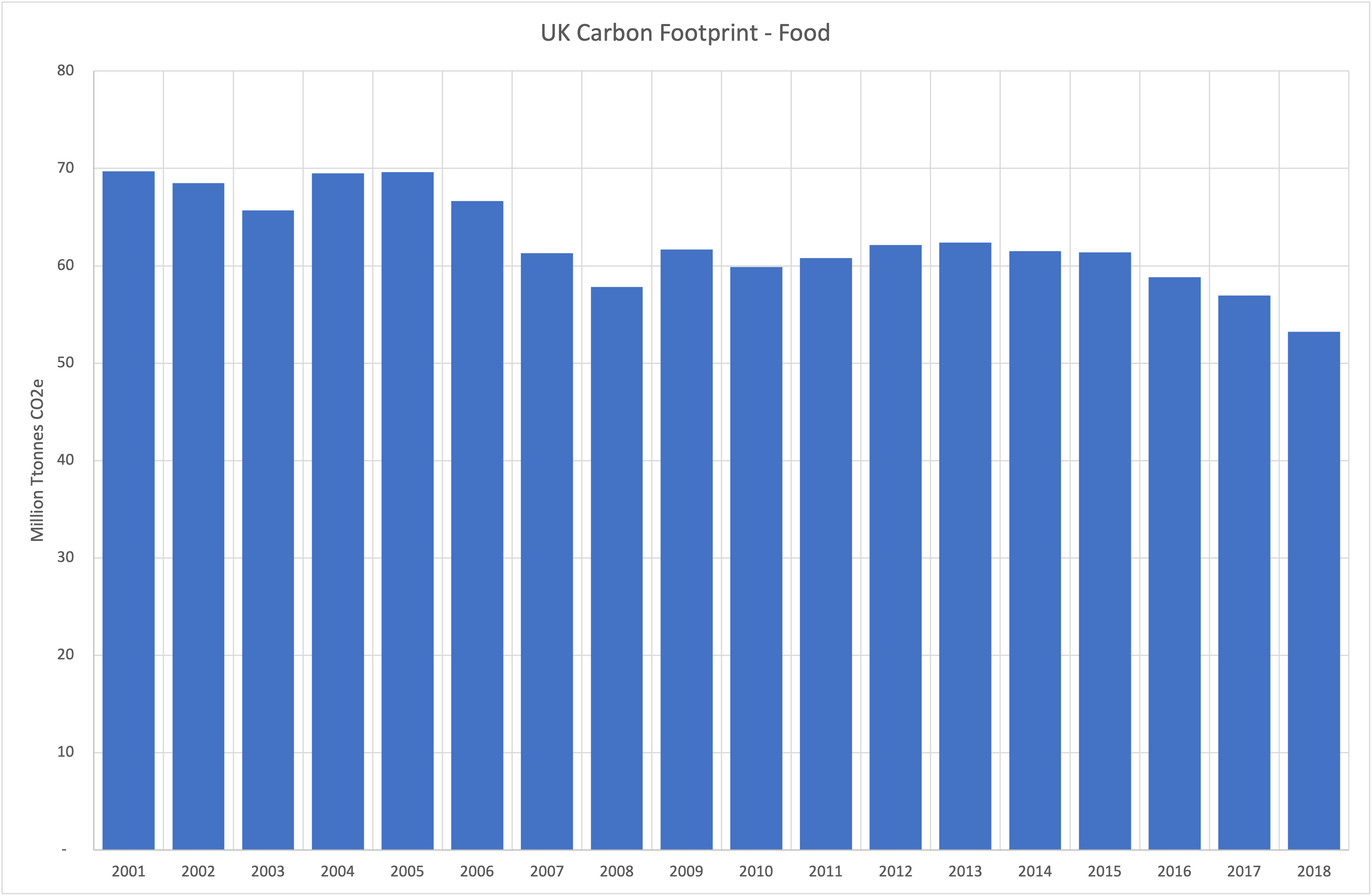
Carbon Footprint: The UK Carbon Footprint of food on a consumption basis is 53 million tonnes of CO2e. Please see graph below:-
Statisitcs:
- Food waste from all sectors is around 10.7 million tonnes.
- This had a value of over £22 billion a year.
- The food that could have been eaten would make over 15 billion meals.
Causes of Food Waste
Consumer Behavior: Overbuying, improper storage, and expiration of goods in households contribute to significant food waste.
Supply Chain Issues: Losses occur during harvesting, transportation, storage, and processing.
Retail Practices: Retailers may discard products due to cosmetic imperfections, overstocking, or expiration dates.
Environmental Impact
Resource Depletion: The production of uneaten food consumes resources such as water, land, and energy.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Decomposing food waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Social and Economic Consequences
Economic Losses: Wasted food represents a loss of resources invested in its production, impacting economies at various levels.
Food Insecurity: While food is wasted, millions of people worldwide suffer from hunger and malnutrition.
Initiatives and Solutions
Reducing Waste in Supply Chains: Improving infrastructure, storage, and transportation can minimize losses during production and distribution.
Consumer Awareness: Education campaigns can promote responsible shopping, proper storage, and mindful consumption.
Policy Measures: Governments and businesses can implement regulations and incentives to reduce food waste.
Technological Innovations
Food Preservation Technologies: Advancements in preservation methods can extend the shelf life of food.
Smart Packaging: Innovations in packaging technology help monitor and control freshness, reducing spoilage.
Community and Individual Actions
Donation and Redistribution: Initiatives that redirect surplus food to those in need can make a substantial impact.
Composting: Turning food waste into compost can be an environmentally friendly way to manage organic waste.
Conclusion
Efforts to address food waste require collaboration across sectors, from individuals and businesses to governments and international organizations.
Raising awareness, changing behaviors, and implementing sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating the impacts of food waste on society and the environment.